More and more dentists are requesting their patients sign a dental extraction consent form before they perform an extraction or complete invasive dental work, such as extractions and other dental work. Dentists have found that many patients do not understand the risks associated with the procedure, and they need to find ways to better inform their patients before performing this type of dental work.
Many patients are in a lot of pain and just want the procedure to be completed; however, it is always a good idea to take a moment to understand the procedure and the risks associated with a dental extraction. This post explains what a dental extraction form is, why it is important, and what you should look for when preparing a dental extraction consent form or if you are being asked to sign one before tooth extraction.
What Is a Dental Extraction Consent Form?
From a legal standpoint, a dental extraction consent form is meant to protect both the patient and the dentist. It describes the procedure the patient is about to be subjected to and the associated risks of the procedure. The patient, after reviewing the form and considering the risks vs. benefits, can decide to proceed or seek some other solution. They can make an informed decision about the procedure.
Once the patient has read and understood the consent form, they sign and date the document, which provides some legal protection for the dentist. It does not protect the dentist from negligence in the performance of the procedure.
Many dental extraction consent forms have space for the patient’s signature only. The dentist needs to be identified and there should be no reason for the dentist to be unwilling to add his signature to the document.
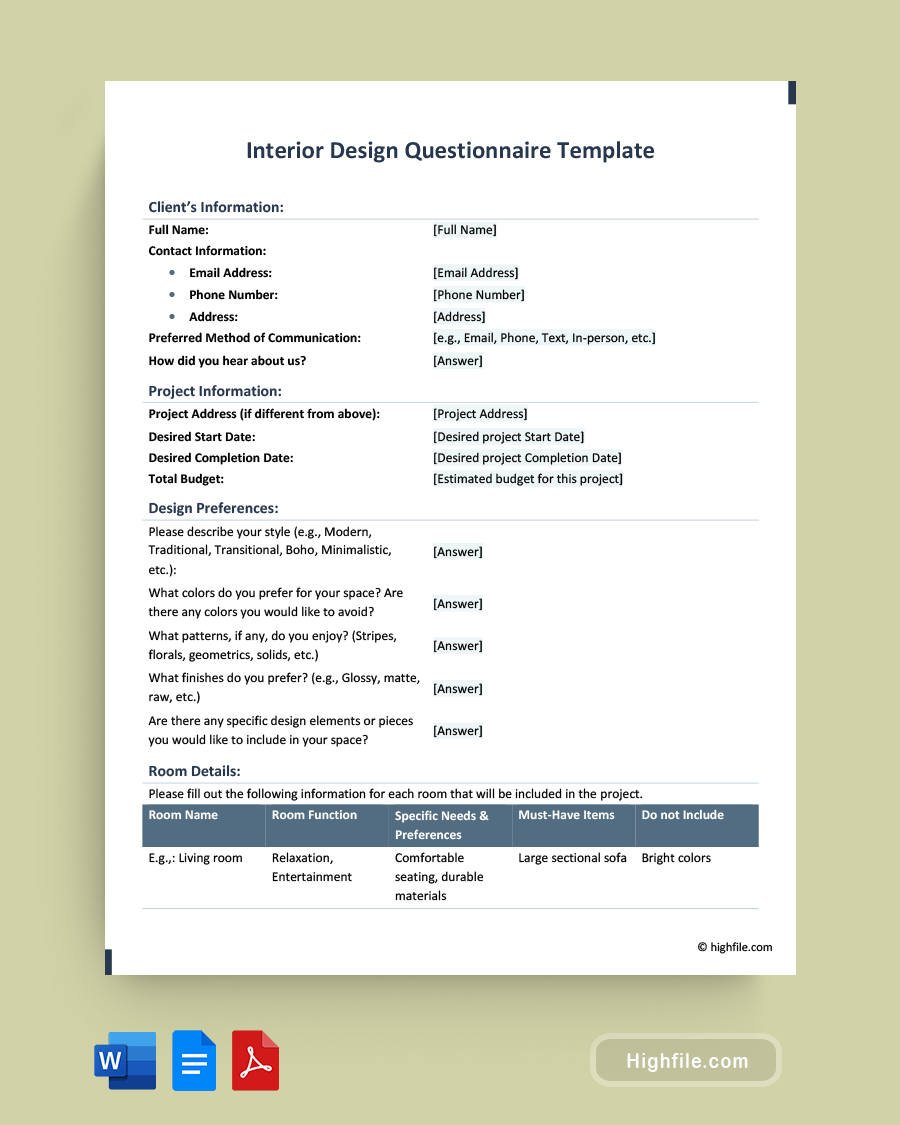
A dental consent form consists of three major sections. The first section identifies the patient and provides contact details including mobile phone, email, and address. The letterhead of the consent form should include the dental practice, address, and contact details.
The second major section covers all of the potential risks associated with the procedure. It is important to read and understand this section. Don’t hesitate to ask questions if you do not understand the language.
The third major section is where the patient indicates they have read and understood the procedure and the risks and are prepared to proceed. Their signature and date should be included along with the signature and date of the dentist.
Why is a Dental Extraction Consent Form Important?
Dental extraction consent forms are important for many reasons and apply to both the patient and the dentist.
Important items for the patient:
- Explanation of the procedure
- Cost or estimate of the procedure
- Identified risks associated with the procedure
- Enhances communication between the dentist and the patient
- Important items for the Dental Office
- All parties have written documentation about the procedure, that the patient consented to
- Establishes credibility in a legal sense in the event there are claims
- Enhances communication between the patient and the dentist
- Patient has the opportunity to ask for clarification about the procedure and risks
- Identifies all of the potential risks associated with the procedure.
Essential Elements of a Dental Extraction Consent Form
The essential elements of a dental extraction consent form should include the following details:
- Dental or clinic identification and contact information
- Patient Identification
- First and last name
- Phone numbers
- Full address including ZIP or Postal code
- Potential Risks (Inherent risks, but not limited to)
- Nerve injury
- Swelling, bruising, and bleeding
- Dry socket
- Sinus impact
- Infection
- Fractures to the jaw, roots, bone fragments
- Injury of adjacent teeth and/or fillings
- Bacterial infections
- Reactions to medication
- Patient Acceptance and Signature
- Acknowledge understanding
- Questions were answered to their satisfaction
- Assume all risks
- Signature of patient and date
- Signature of dentist and date
The actual wording of the consent form is based on the jurisdiction the dental office operates in and the specified procedures that may be applied, including simple extraction or surgical extraction.
FAQs
Pre-extraction instructions will depend on the dentist and whether you are having the extraction completed with or without anesthesia. In general, the following are guidelines many dentists follow; however, always apply the specified guidelines provided to you by your dentist:
ᐅ Share your complete medical history with the dentist, including medications, immune system status, artificial joints, mechanical valves, heart conditions, sleep apnea, liver disease, etc.
ᐅ Most dentists will recommend you stop taking blood thinners for several days before and after the procedure
ᐅ Discuss which anesthesia will be used and if you have any interactions
ᐅ Discuss which painkillers to have on hand after the surgery
ᐅ Avoid eating for 12 hours before the surgery if you are having anesthesia
ᐅ Stop smoking at least 12 hours before the surgery
ᐅ Review your insurance coverage to avoid surprises with unexpected expenses
ᐅ Whether you have anesthesia or local freezing of the gum and jaw, plan for someone to drive you home and get you situated at home with the appropriate medication
ᐅ Dress comfortably
ᐅ Remove all jewelry, including contact lenses
ᐅ Avoid perfumes, body sprays, and lipstick
Post-op instructions will vary depending on the specific surgery or procedure completed and the dentist’s assessment of what is needed in your situation. In general, the following post-op instructions should be considered:
ᐅ Keep the surgery site clean. Rinse and gargle with antimicrobial mouthwash two to three times a day, focusing on the extraction site.
ᐅ Take all pain and antibiotic medications recommended by the dentist
ᐅ Do not operate vehicles or machinery while on pain medication
ᐅ Avoid strenuous activities for a minimum of two days
ᐅ Consume soft foods and avoid chewing food
ᐅ Your tongue will still be difficult to feel for a while, be careful to avoid accidentally biting into your tongue
ᐅ Anyone experiencing shortness of breath, bleeding, swelling, chills, fever, vomiting, or nausea should follow up with your dentist immediately since this could indicate an infection.
Simple extraction and surgical extraction are the two types of extractions performed on patients.
A simple extraction is completed usually in the dental office with a local anesthetic to manage the pain experienced by the patient. The dentist will pull the visible tooth using several dental instruments, including elevators and forceps.
A surgical extraction is used when the tooth is not fully exposed, broken, or below the gum line. The procedure is potentially longer, more difficult, and can be painful. Anesthesia is preferred by both the dentist and most patients. The surgery must be performed in the presence of an anesthesiologist with the appropriate monitoring equipment available.
A surgical extraction is also used when the patient requests an anesthesiologist due to their concern about the procedure.
Although your jaw will still be frozen, and you should not be in significant pain, there will be a great deal of discomfort, making it difficult to focus and concentrate on driving. Many dentists will suggest that a friend drive you home and help manage any pain medication you need after dental extraction.
Conclusion
There are two types of dental extraction. Simple extraction involving local freezing of the jaw is performed in the dentist’s office, and surgical extraction with an anesthetic with the appropriate monitoring equipment to monitor the patient’s vitals during the procedure.
Patients should not drive after either procedure due to the effects of the anesthesia and/or pain medications they may be given.
Patients should read, understand and ask questions about the procedure and the consent form before adding their signatures to the form. The consent form relieves the dentist from any spurious lawsuits associated with the potential side effects. However, the consent form does not offer protection to the dentist for negligence in the performance of the dental extraction.
Always follow the pre-extraction and post-extraction guidelines to guarantee the best outcome, avoid infection, and heal quickly. Failure to follow the instructions can result in serious health issues, including pain and infection of the extraction area and jaw.